Monetizing With Payments: A Guide for ISV and SaaS Businesses
Sabine Konhaeuser2023-05-03T12:44:33-04:00
Introduction
Payment technology is presenting new opportunities for today’s Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies. With the introduction of frictionless payment solutions like mobile wallets and one-click checkout flows, payment processing is playing a bigger role in the end-user experience. As a result, non-financial software companies have a lot to gain by partnering with a Merchant Services Provider (MSP) and integrating payment tech within their applications. Not only can these businesses achieve greater control over the customer experience and improve brand loyalty, but they also enjoy an additional revenue stream by way of payment processing revenue. As more and more customers come to expect embedded payment flows, ISV and SaaS companies must adapt in order to satisfy market demand.
If you are currently considering a payment monetization strategy, then this white paper is a must-read. We’ll walk you through what it means to monetize with payments, why this strategy is growing in popularity, and what your options are for getting started.

Read the full white paper anytime and anywhere.
What Is Payment Monetization?
The payment processing landscape is filled with a wide range of players and entities — and those that are directly involved in the payment processing cycle earn a portion of processing fees that are charged to the merchant. By entering into a partnership with one of these industry players — a Merchant Services Provider — ISVs and SaaS companies have the ability to carve out a corner in this crowded payment space and earn a cut of processing fees.
There are several paths to payment monetization, each with varying revenue-sharing models and technological capabilities. But before diving into these various revenue-sharing models, let’s first take a closer look at payment processing fees: their purpose, who they’re paid to, and what they’re made up of.
Payment Processing Fees Explained
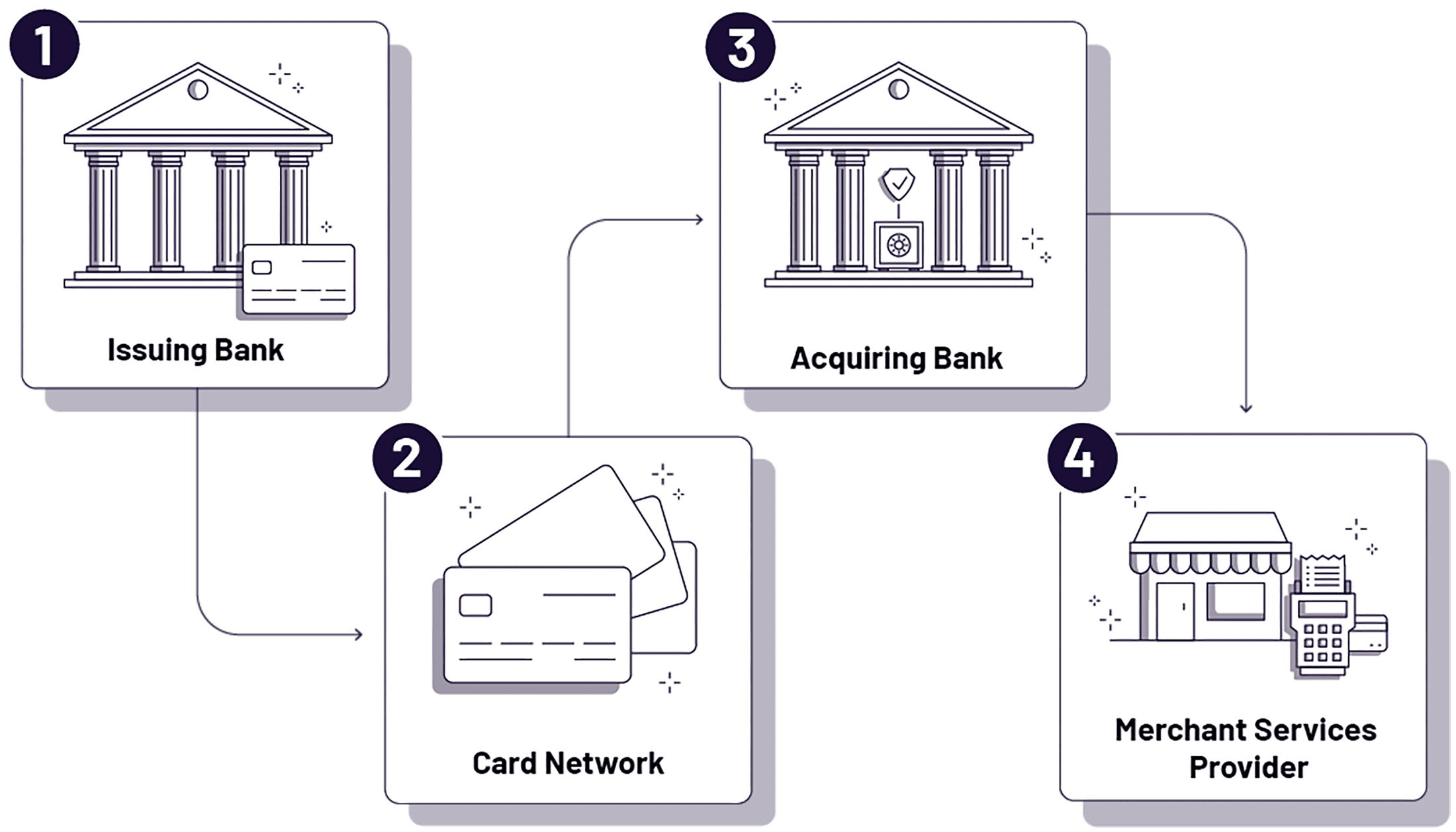
Payment processing fees serve two main purposes: to cover overhead costs and offset the risk associated with credit card payments.
There are four key players who facilitate the transaction process, and to that end, they each take a portion of the transaction costs. These parties are:
- The Merchant Services Provider
Merchant Services Providers set up merchants with processing accounts, provide them with the necessary technology to accept payments, and collect processing fees. They distribute collected fees to the issuing bank and card network (as well as any other participating parties).
There are various types of Merchant Services Providers (MSPs), including Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs), Payment Facilitators (PayFacs), banks, and other financial technology companies. While some overlap exists among these entities — in terms of their functional descriptions and the services they offer — the important thing to remember is that the MSP’s primary role is to allow businesses to effectively process payments.
- The Issuing Bank
This is the bank that issues the customer’s credit card — for example, Bank of America or Chase. They assume the largest amount of risk, as they lay out the funds for the purchase and ultimately have to collect it from the cardholder.
- The Card Network
Mastercard, Visa, American Express, and Discover are the four major card networks (also known as card brands). Note that American Express and Discover serve two roles: they function as both card networks and issuing banks.
- The Acquiring Bank
The acquiring bank is the merchant’s bank that processes payments on behalf of the merchant and funds their account. Fiserv and Worldpay are two of the biggest acquiring banks, but there are many others.
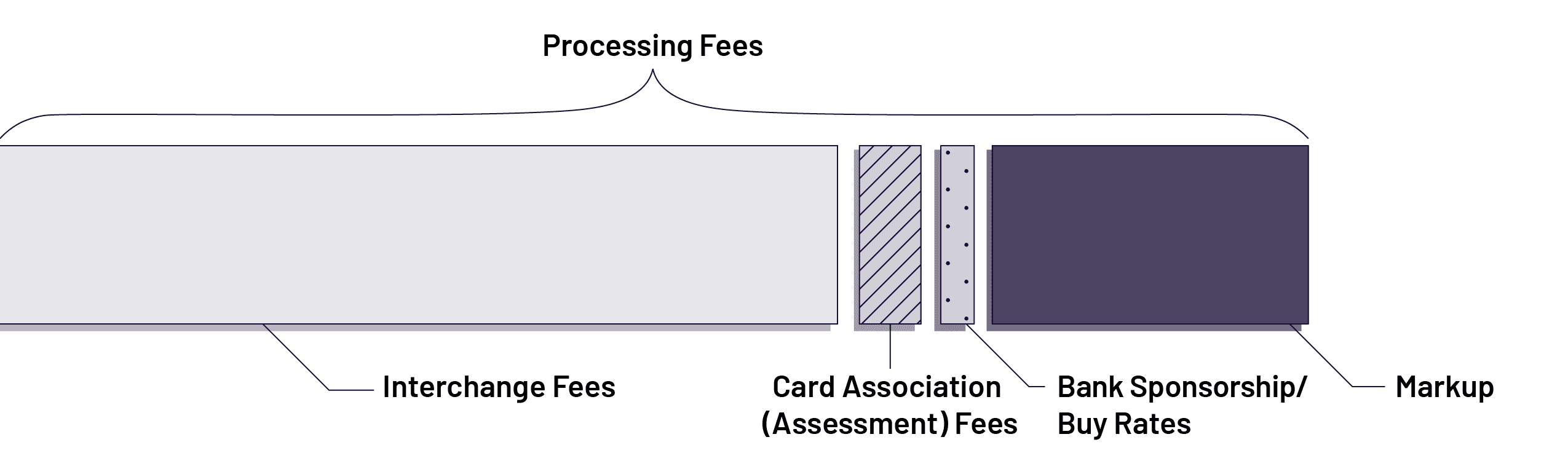
What’s Included in Processing Fees?
Merchant Services Providers use several different pricing structures to calculate and collect costs. These include flat-rate, tiered, bill-back, and pass-through models, some of which you may already be familiar with. (The details of these structures are complex and beyond the scope of this white paper.) However, as you will learn later on, one of the benefits of new PayFac solutions is that they typically employ simple flat-rate pricing.
The amount that merchants see on their monthly statements is an accumulated total of various different fee types. There are three main processing fee categories:
- Interchange fees
The card associations issue new interchange rate schedules twice every year. These schedules map out hundreds of different interchange rate categories and their associated fees. The fees are typically structured as a percentage and per-item fee.Every transaction is assigned a rate depending on which category it qualifies for. This is determined based on a variety of factors that relate to the risk level of the transaction (such as industry, card-present vs. card-not-present) or the type of card (e.g., business cards, rewards cards, etc.).
These interchange fees are set by the card association. The issuing banks receive the largest percentage of these fees because 1) they take on the most risk, and 2) they provide incentives to cardholders through various rewards programs.
- Card Association (Assessment) Fees
Assessment fees are paid to the card networks — such as Visa/MC, American Express, and Discover — to cover operational expenses.
- Bank Sponsorship/Buy Rates
The buy rate is charged by the acquiring bank to the MSP, who passes it along to the merchant. These fees are minimal compared to interchange and card association fees.
- Markup
MSPs mark up the bottom-line processing fees to recover overhead costs and earn a profit.When an ISV or SaaS company partners with an MSP (or becomes an MSP), their profit comes from this markup. In addition to this new revenue stream, their users and clients also benefit from the specialized services and support that the MSP provides.
Sample Breakdown of a $100 Transaction
Let’s look at an example where a consumer makes a $100 purchase. Assuming 3% processing fees, the merchant will receive $97, and the other $3 will be broken down and distributed by fee type, as in the below example.
Sample Processing Fee Distribution
| $1.75 | Interchange Fees | |
| $0.20 | Card Association Assessment Fees | |
| $0.10 | Bank Sponsorship/Buy Rates | |
| + | $0.95 | Markup |
| $3.00 | Total |
Getting Started With Payment Monetization
Now that you have a better understanding of processing fees, let’s discuss how you — as an ISV or SaaS — can earn a profit from them. Specifically, there are two main paths to payment monetization: referral partnerships and the PayFac model.
The Traditional Approach: Referral Partnerships
As discussed above, MSPs provide merchants with processing accounts and mark up baseline fees to earn a profit. By entering into a referral partnership with an MSP (most commonly an ISO), the ISV or SaaS company is able to earn a portion of the markup.
Referral partnerships have been the primary payment monetization path for several years, attracting software companies in verticals ranging from brick-and-mortar retail, amusement and recreation, e-commerce, healthcare, and more. With this model, the ISV or SaaS partner earns a portion of processing fees on transactions that originate through their software. This incentivizes the ISV or SaaS partner to bring on more merchants, and it’s a win-win situation for both parties.
A key advantage of the referral partnership approach is that the burden of managing the end user’s payment processing account is offloaded to the MSP. They oversee onboarding, rate review, equipment deployment, tech support, and much more. Of course, when it comes to partner and customer support, there’s a great degree of variation among MSPs and payment technology providers — so it’s important to keep this in mind when looking for an MSP partner.
Another benefit of referral partnerships is that the MSPs often lead sales and marketing efforts. They typically have dedicated sales teams who interface with your current users or leads and expertly present the benefits of their payment solution. They also often provide marketing collateral such as flyers and co-branded sales pages.
The Evolution of Merchant Services
A new approach to merchant services is changing the way that some ISVs and SaaS companies monetize with payments. Due to technological advances and greater awareness of the lucrative power of payments, non-financial companies are increasingly opting to become merchant services providers (MSPs) themselves. Although traditional channels – whereby merchant services are provided by an ISO – are still the right fit for some businesses, ISV/SaaS provision of merchant services is on the rise.
This shift has been coined “software-led payments.” More and more, merchants are being introduced to payment processing functionality through their business’s software provider, such as their POS system, accounting software, or e-commerce platform. Data from Mercator Advisory Group reveals that the number of small businesses that will receive direct merchant services through an acquiring bank or merchant bank is estimated to drop to just 31% in 2025 — down from 59% in 2017.
The Shift Toward Embedded Payments and the PayFac Model
In their quest to become MSPs, ISVs and SaaS companies are embracing technologies that allow them to embed payments within their software. This phenomenon, known as embedded payments, is taking the software world by storm. From food services apps like Starbucks’ that support storage of payment methods, to healthcare patient portals with integrated bill pay, the use cases of embedded payments are endless.
The embedded approach provides incredible benefits to all involved parties. The ISV or SaaS company gains a competitive advantage by offering a cutting-edge feature set, and they grow their revenue from payment residuals. Merchants enjoy improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, while their customers benefit from a seamless experience in which making a payment is part and parcel of the overall brand interaction.
Payment Facilitation: The Embedded Approach
Payment facilitation (PayFac) is the engine that drives embedded payments. This new model improves upon the traditional approach by allowing ISVs and SaaS companies to become MSPs and integrate sleek, embedded payment functionality within their software.
There are several options for becoming a PayFac. No matter which option the ISV or SaaS business chooses, they will need to open a direct account with an acquiring bank, enabling them to provide payment processing services as a master merchant account provider. In turn, their merchant clients are onboarded as sub-merchants under the master account. In contrast, merchants who obtain payment processing services from an ISO (as is typically the case with referral partnerships) will need to open their own accounts with an acquiring bank.
Traditionally, it was the banks that did the underwriting and assumed the risk of payment fraud. Under the PayFac model, these risks are assumed by the PayFac. This means that when an ISV or SaaS company becomes a PayFac, they also become financially responsible for any fraudulent activity that they or their merchants encounter. Fortunately, there is an alternative to this that allows ISV or SaaS companies to offer a PayFac solution without assuming risk. This is known as PayFac-as-a-Service (PFaaS), which we will discuss in a later section.
There are a number of benefits of the PayFac model for ISVs and SaaS companies. Most notably, PayFacs can be very lucrative, as residuals are not being shared. Data from Infinicept reveals that software companies that become PayFacs can increase their revenue by as much as 14 times and increase their valuation by as much as 127 times!
Additionally, as a PayFac, you have much greater control over the end-user experience. You’ll have full development control over the entire payment stack and the flexibility to design interfaces and checkout flows all per your precise specifications.
The Benefits of the PayFac Model for Merchants
ISVs and SaaS companies enjoy greater customer loyalty and retention once they become PayFacs — and for good reason. As a PayFac, you’ll be able to pass along incredible benefits to your merchant clientele, such as:
- Simple Flat-Rate Pricing
PayFac solutions employ flat-rate pricing structures, rather than the more complicated traditional models. The benefit of flat-rate pricing is that it’s easy for merchants to understand and is incredibly transparent, allowing them to easily forecast expenses and plan for overhead costs. - Fast, Seamless Onboarding and Account Approvals
Because the ISV or SaaS company owns the underwritten merchant services account, they’ve done all the heavy lifting. When signing up for a processing account with a PayFac, the merchant only needs to provide a few key data points to get up-and-running fast.
- Cutting-Edge Technology
Today’s PayFac solutions feature next-generation payment processing technology that’s not always offered by ISOs — such as support for the latest payment methods, mobile-friendly processing, sleek hardware options, and much more.
Becoming a PayFac: The Traditional Path
Most ISVs and SaaS companies don’t have the time, funds, or resources to embark on the traditional path to PayFac. Fortunately, an alternative option has arrived on the market in recent years. PayFac-as-a-Service (PFaaS) solutions — also known as managed PayFacs — are out-of-box solutions that equip businesses with the full infrastructure and feature set they need to become PayFacs. PFaaS solutions like Cardknox Go include software and APIs (both for internal management and end-user interfaces), compliance, risk monitoring, and much more. ISVs and SaaS companies who choose the PFaaS route enjoy all the key benefits of the PayFac model while benefiting from rapid time-to-market, reduced risk burden, significantly lower expenses, and simplified scope of development.
PayFac-as-a-Service: The New Path to PayFac
Most ISVs and SaaS companies don’t have the time, funds, or resources to embark on the traditional path to PayFac. Fortunately, an alternative option has arrived on the market in recent years. PayFac-as-a-Service (PFaaS) solutions — also known as managed PayFacs — are out-of-box solutions that equip businesses with the full infrastructure and feature set they need to become PayFacs. PFaaS solutions like Cardknox Go include software and APIs (both for internal management and end-user interfaces), compliance, risk monitoring, and much more. ISVs and SaaS companies who choose the PFaaS route enjoy all the key benefits of the PayFac model while benefiting from rapid time-to-market, reduced risk burden, significantly lower expenses, and simplified scope of development.
Monetize Payments With Cardknox
With its ability to elevate the user experience, payment processing technology poses an incredible opportunity for software businesses. By tapping into the world of payments, ISVs and SaaS companies can create app interactions that drive loyalty and engagement — and at the same time, supercharge their earnings. As customers increasingly demand embedded payment flows, now is the time to start monetizing payments.
Cardknox has developed a suite of tools and services that make it easy for ISVs and SaaS companies to grow their revenue and deploy integrated payment functionality for in-store, online, and mobile channels. We offer a traditional referral partner program as well as our PayFac-as-a-Service solution, Cardknox Go.
As a Cardknox partner, you’ll enjoy powerful APIs and SDKs for the most seamless payment integrations, incredible support, and competitive residuals. To learn more about our advantages, visit www.cardknox.com/partner-program.

Read the full white paper anytime and anywhere.